The Evolution and History Of Mutual Funds In India
26 October 2021
The mutual fund in India offers new and well-established investors an intriguing option of investment vehicles since it is highly diversified. Diversification reduces investment risk to a greater extent. Before moving further, let's briefly learn about the history of mutual funds in India.
As you already know, a 'mutual fund' is a vehicle for investing that allows several individuals to combine their resources to buy stocks, bonds, and other assets. The combined holdings of stocks, bonds, and other assets the fund owns are called a portfolio. The mutual fund portfolio is structured and maintained to correspond to the investment goals specified in its prospectus. These funds are managed by money managers or fund managers whose primary intention is to provide maximum returns to investors by investing in securities that are in sync with the fund's objective.
History of Mutual Funds in India
The history of Mutual Funds goes way back to 1963. The Unit Trust of India was the first firm to start mutual funds. It was established by the Reserve Bank of India and the Government of India as a joint venture in 1963. The UTI's goal was to let small, uninformed investors acquire equity and other financial instruments in larger companies. At that time, UTI had a monopoly. The 1964 Unit Scheme was one of its mutual fund products, which operated for several years.
The history of mutual funds is broadly divided into four phases:
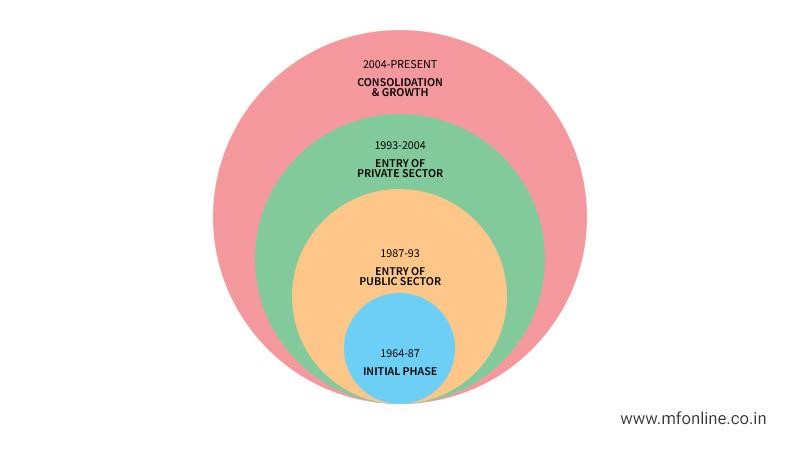
Mutual Fund History First Initial Phase: 1964-1987
- Unit Trust Of India was set up in 1963 by an Act of Parliament
- It was set up by the Reserve Bank of India under its regulatory and administrative control
- The first scheme launched by UTI was the unit scheme 1964.
- The RBI was de-linked from UTI in 1978, and IDBI took over the regulatory and administrative control in place of RBI.
- UTI had Rs. 6,700 asset crores under management at the end of 1988. (AUM)
The history of mutual funds in India is as amusing as any other startup.
Mutual Fund History Second Phase: 1887-1993
- Non-UTI mutual funds from the public sector entered the market in 1987. Public sector banks, LIC and GIC, have established these.
- The first non-UTI Mutual Fund was set up in June 1987 by the SBI Mutual Fund. After that, Canara Bank followed suit, and in December 1987, Canara Bank Mutual Fund came into existence.
- During the second phase, some other funds that came into existence were Punjab National Bank Mutual Fund (Aug 89), Indian Bank Mutual Fund (Nov 89), Bank of India (Jun 90), Bank of Baroda Mutual Fund (Oct 92)
- At the end of 1993, the mutual fund industry had assets under management of Rs 47,004 crores.
The second phase was all about the entry of the Public Sector into the mutual fund industry. Observers from this sector claim that not only did the foundation of the industry expand in the second stage, it also encouraged investors to invest more in mutual funds. As a result, the mutual fund sector in India was obviously on the brink of more significant expansion.
Mutual Fund History: Third Phase 1993-2003
- A new era began in the Indian Mutual Fund Industry with the introduction of private sector funds in 1993, giving Indian Investors a wide choice of funds.
- It was also in the same year that all mutual funds were governed and registered under SEBI. The primary function of the board was to protect the interests of the investors.
- Later in 1996, the regulations were replaced by more comprehensive and revised rules. Thus, as of now, the industry functions under SEBI regulations 1996.
- In the third phase, the industry witnessed several mergers and acquisitions that resulted in the growth of mutual fund houses.
- There were 33 mutual funds with total assets worth Rs 1,21,805 crores at the end of January 2003.
The government of India understood the need to liberalize the Indian economy in the period 1991-1996. Reforms in the financial industry have been hour-needed. To restore the economy, India required engagement from the private sector.
With this in mind, the government also allowed the private players into the mutual fund business. It was a good step for international companies, and they joined the Indian market in large numbers. During this time, 11 private players started their asset management funds in cooperation with overseas companies.
Mutual Fund History Fourth Phase: 2003-2014
- UTI was divided into two distinct organizations in February 2003, after abolishing the Unit Trust of India Act 1963. The first is the Specified undertaking, which, at the end of January 2003, was responsible for the activities of the US 64 scheme, assets under management of Rs 29,835 crores, and some other schemes.
- The Specified Unit Trust of India operates under an administrator and regulations set by the Indian government and does not fall under the authority of the Mutual Fund Regulations.
- The second is the UTI mutual fund carved out of Unit Trust of India as SEBI registered mutual fund from February 1, 2003.
- The fund house mentioned above was sponsored by SBI, LIC, PNB, and BOB.
- In March 2000, with the bifurcation of the erstwhile UTI, which had more than Rs. 76,000 crores of assets under management and with the setting up of UTI mutual fund, conforming to the SEBI regulations and with mergers taking place between private sector organizations, the mutual fund industry proceeded towards its consolidation phase.
Current Status of Mutual Fund Industry
The Indian Mutual Fund Industry's assets under management were Rs.36,73,893 on September 30, 2021. In the span of 5 years, from September 30, 2016, to September 30, 2021, the Mutual Fund Industry's Asset Under Management has grown from Rs. 15. 80 trillion to 36.74 trillion, respectively.
Conclusion
While the history of mutual funds began in 1963 by the Unit Trust of India, this industry has evolved from being controlled by UTI to balanced public and private participation. Compared to global standards, the Indian mutual fund sector is exceptionally tiny. However, this industry can develop multiple-fold with more significant support from AMFI and the government.
Disclaimer: All mutual funds are subject to market risk. Read all scheme-related documents carefully.



